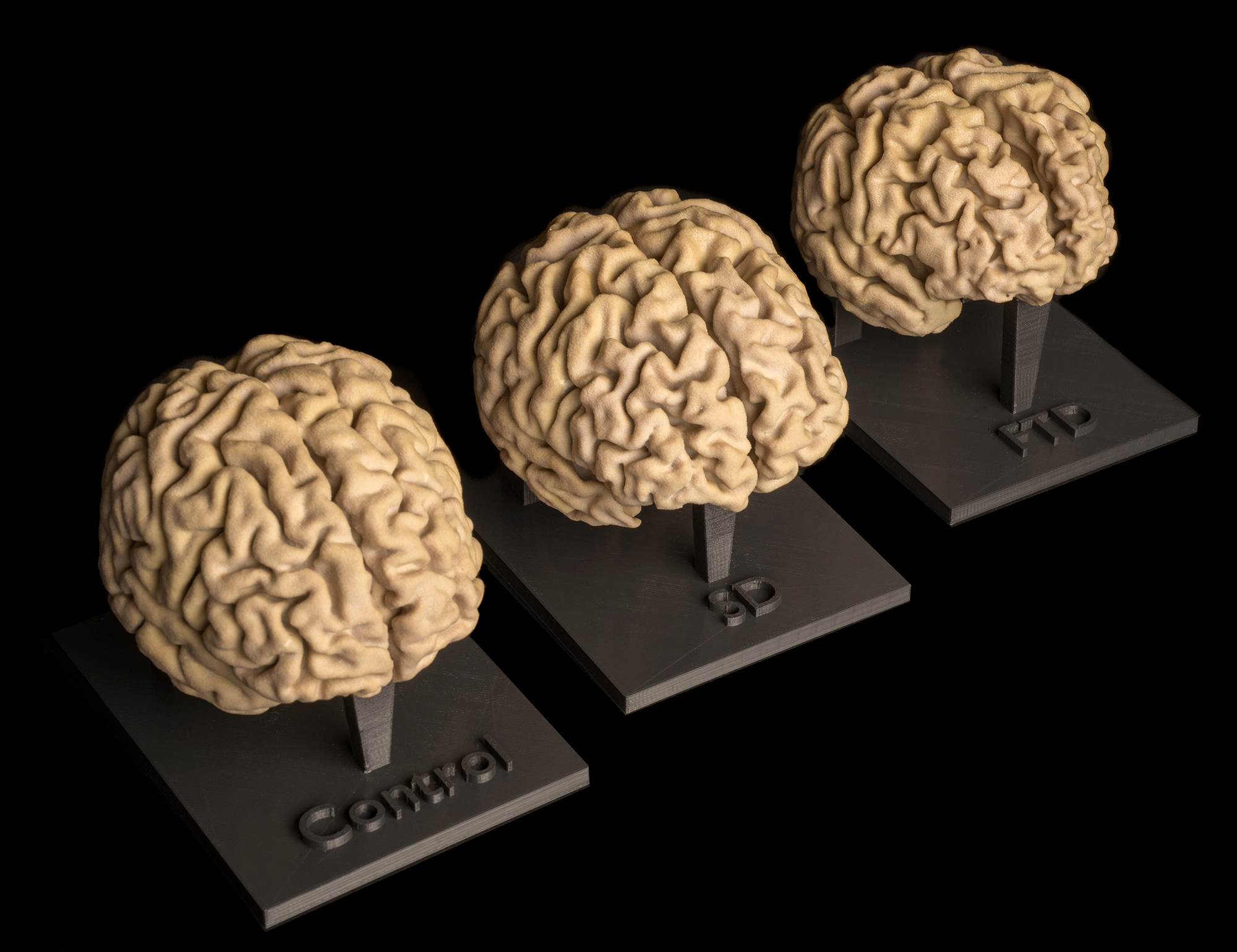
Rapid, accurate, full-colour 3D Printing in Media Studio
Also known as additive manufacturing (AM), this rapidly advancing technology has many applications in medicine, surgery and biomedical science. 3D prints can be made in a wide range of materials, including plastics, resins, hardened plaster and various metals. See some examples below and contact us to find out how AM can help you.
Download our 3D Printing Factsheet: ![]() 3DPrintFactsheet2.pdf
3DPrintFactsheet2.pdf
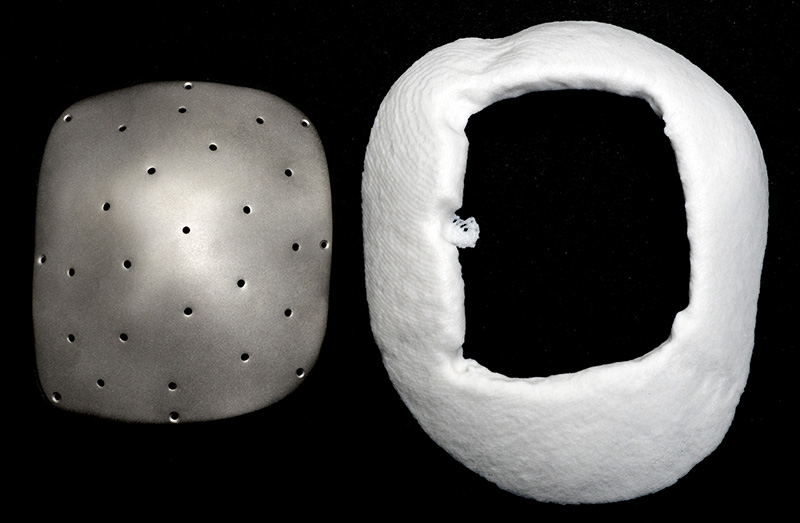
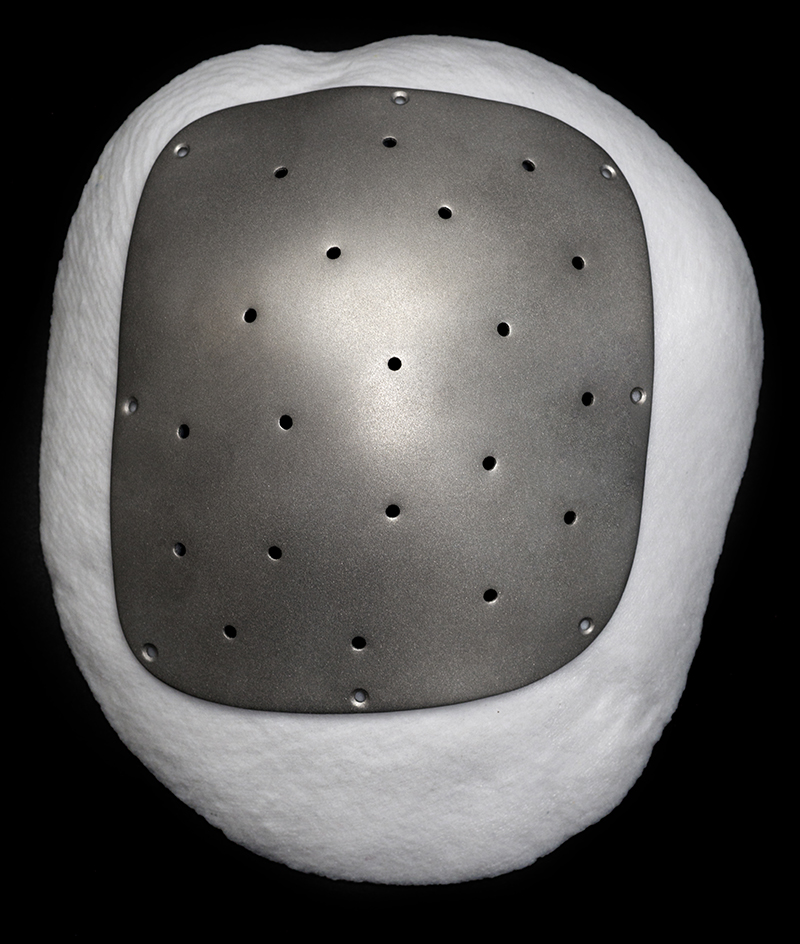

Titanium cranioplasty plate: L) The titanium cranial plate is printed using a laser sintering technique, which is a form of additive manufacturing (3D printing), and finished to a smooth surface with rounded edges. The holes around the perimeter are designed precisely to fit the surgical screws with which the plate is attached to the skull. Other holes permit fluid transfer and the suturing of structures around the brain to the plate. R) A hardened plaster model of the patient’s skull defect, derived from CT data, was used to confirm the accuracy of the plate’s conformity to the skull’s contours.
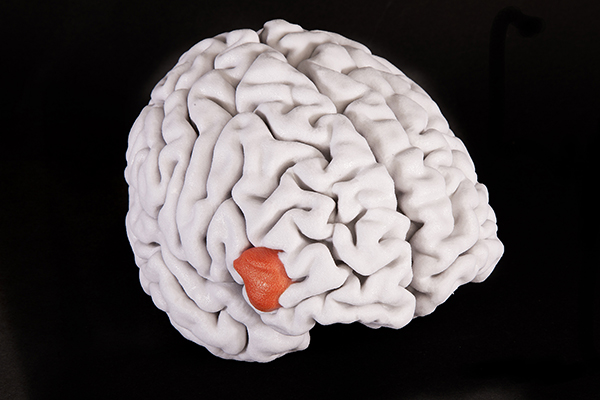
Model of brain showing a tumour in the right hemisphere; derived from MRI data (model segmented by Neurosurgeon, Mr Mike Hart).
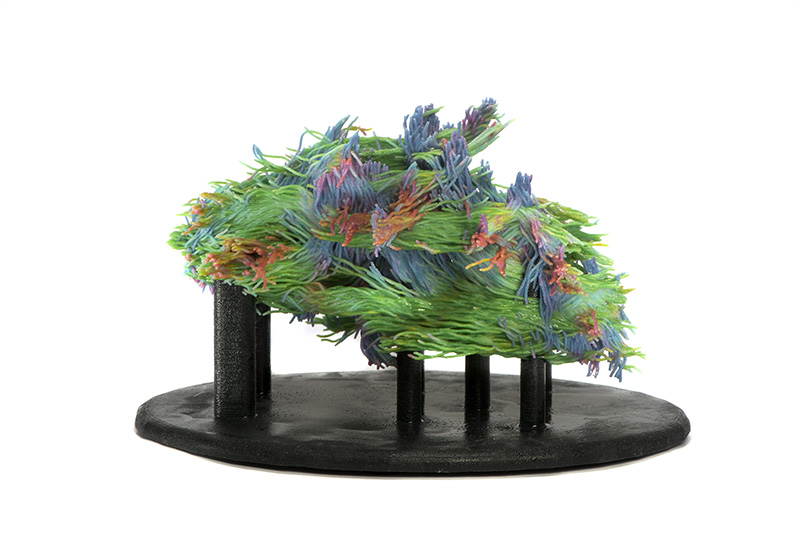

Brain coonectome, showing white matter tracts visualised by MRI Tractography (Mr Mike Hart).
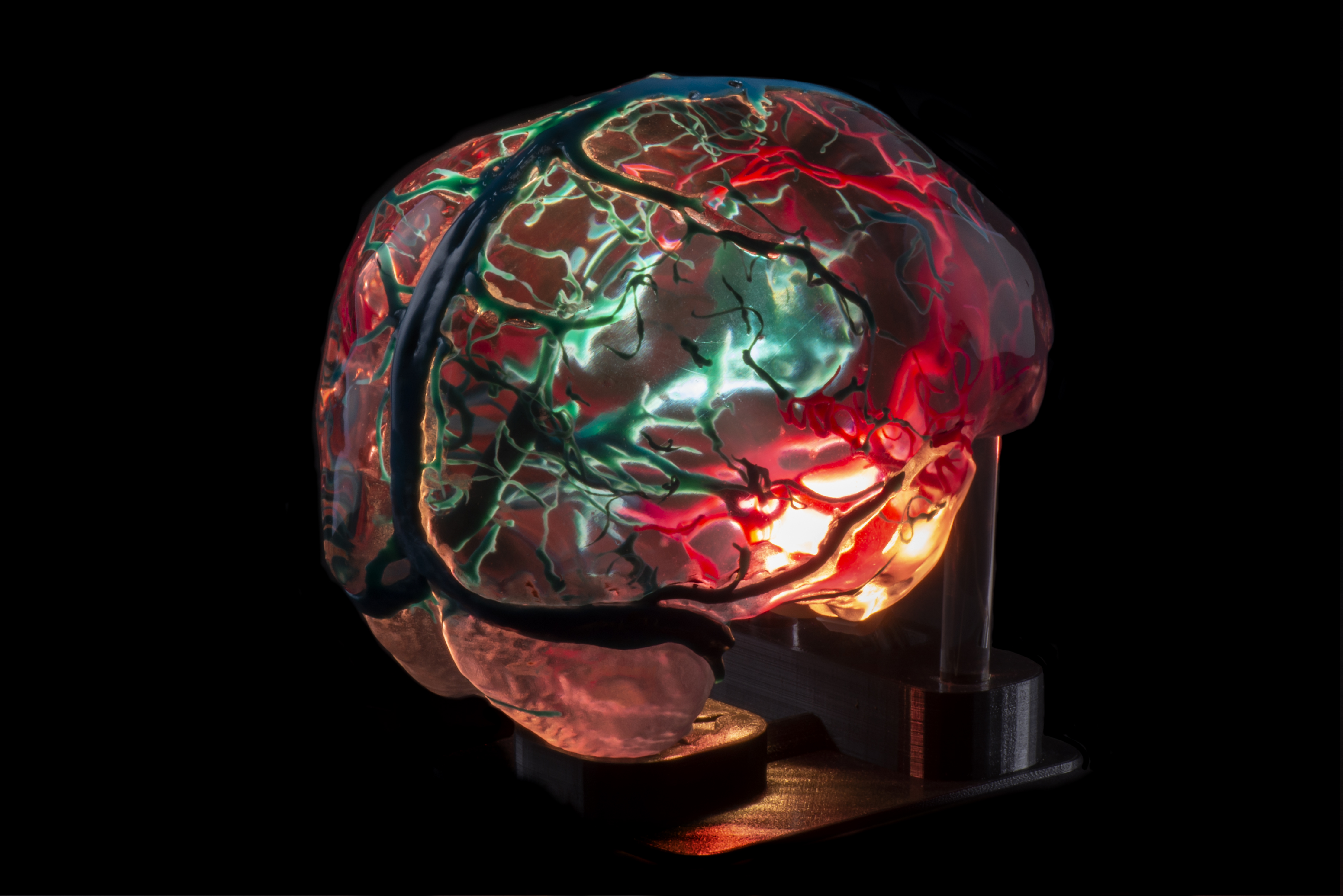
Brain vasculature showing arteries (red) and veins (blue)
Soft tissue segmentation
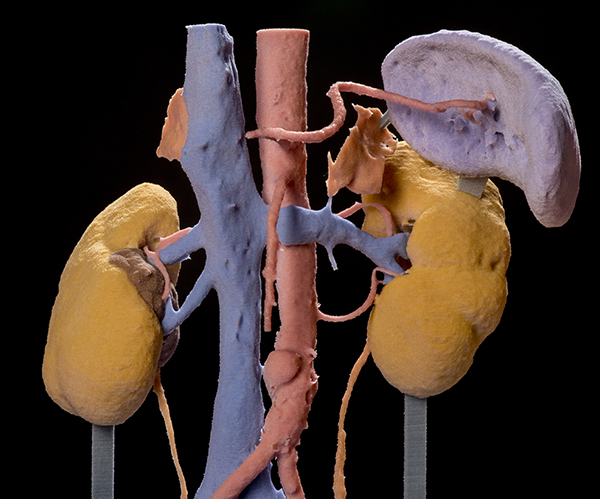
Vasculature of kidneys (with a cyst on the R kidney)

Various parts manufactured with low-cost FDM printing
Watch a 3D print being made using FDM printing